It’s 2019, I’m 80 miles away from land in the Atlantic Ocean, and I just have to laugh. I just got out of the water and noticed that my camera housing is leaking. I couldn’t afford the Nauticam rental this time, so I went cheap and hoped for the best. It’s my third trip to the Silver Bank with Tom Conlin and Aquatic Adventures and once again my photographic luck was left behind on solid ground.
Oddly, I’m ok with this and it’s time to get back in the water. I grab my phone for some snapshots, slide on belly over the side of the boat and swim over to this mama humpback whale and her calf. Yes, that’s right I’m swimming with humpback whales.
Most of my Whale Tail comes from everything around my three one-week trips to the Silver Bank in 2015, 2017, and 2019. I could tell you all about my trips and the cameras I used, some of that will be mixed in, but this story is more about fear and overcoming obstacles.

The trips themselves were incredible and beyond words. Moments and experiences and friends that have changed my life forever. Memories and stories that most people can’t imagine and a few photographs that don’t capture the moment.
I don’t know where the idea to do this came from — it wasn’t like I especially loved whales as a kid. Growing up, I was never much into adventures. I do believe in animal rights and support those who stand up for our oceans. I am drawn to underwater photographers and the beauty they capture from a world just below my normal vision of the surface. I often purchase their photographs so I can support their incredible talent.
I heard about these “snorkel with whale” trips in a random conversation and decided to try it myself. I booked it and neglected to do any real preparation. I swam in high school gym class and was a good swimmer 30 years ago. Back in the day, that just meant I could swim from one end of the pool to the other without touching the bottom. So, I figured I was okay.
Of course, I researched the important things like underwater cameras, swim fins, wet suits, because the right equipment makes all the difference.
I decided a week before the trip that I should get my feet wet and try some underwater photography. I booked a trip to the Homosassa River in Florida to swim with manatees and discovered as I tried to descend into a six-foot-deep river that I am absolutely terrified of water.
After 10 minutes of clinging to the boat ladder for dear life, a manatee came by to introduce itself. I let go of the ladder long enough to gather my senses and flailed about the river like an injured human. I made so much noise that the manatees and other humans on the trip kept their distance. But at least I thought that had figured out this water thing and was pretty much ready to go.
My 2015 trip was not a success. A six-foot-deep lazy river is a little different than swimming in the Atlantic Ocean. I was scared and seasick, which is not a good combo. I got in the water once and will spare you the details. I spent the rest of the trip with my eyes fixed on the horizon and photographed surface activity.


Even with this limited engagement, I found something I loved. The day I got back home; I sent an email for a request for a date in 2017.
So, with two years to prepare, I again waited until a few weeks before the trip to practice. It was back to the Homosassa River for two days this time. I practiced getting into the water and did a little better once I calmed down. I did research better alternatives to the Dramamine that made me sick and with my motion sickness patches and a new set of fins I was ready to go.
2017 had some crazy storms that came through along with some pretty rough seas. Luckily, the swells were a few inches below the unsafe maximum height for small craft, so we were able to search for whales for four days without any success. We couldn’t even see the blow as the whales surfaced because the wind immediately whisked it away. Then, on the last day about 30 minutes before we had to leave for port, we found a mother, calf, and escort in the shallow 30-foot coral reefs.



I had been waiting for this moment for two years, so when they said go, I slipped into the water without hesitation while at the same time trying not to soil my wetsuit. I immediately panicked but somehow recovered my senses, then swam the best I could toward the whales. I just couldn’t keep up with the others and ended up 20-30 feet behind them. It was far, but I was in the water and seeing my first set of whales.
The next part always brings tears to my eyes when I think of it. I heard Tom yell out, “Lorenzo, grab John and bring him to the front” So Lorenzo (our in-water guide) swims back to me and grabs my arm and swims me up to the front, just past the group, up to ten feet from the mother whale. I start to stutter gasp a little as if I’m about to uncontrollably sob and I feel the tears well up in my eyes for a moment. Just a second. And then I just feel pure joy, like I’m a little boy and the world is magnificent.
I’m just in front of her flipper, her eye is closed, and you can tell she is just relaxing while we babysit her calf. She opens her eye, looks at me, looks at her baby, looks at the other snorkelers and goes back to sleep. The calf comes by and like every other bratty child, biffs her mom’s nose with its tail. With three effortless tail swishes the calf does a full breach out of the water then swims off. The mother and escort follow, and we return to the boat.
As soon as I got home, I sent an email requesting a date for a 2019 trip.
After several months of procrastinating, I signed up for a pool membership in April 2018. I have been swimming laps an hour a day ever since. Around July 2018, I had overcome my fear of water, and by December 2018, I quit smoking because it was interfering with my swimming. By 2019 I was ready to go.
There is always a test run at the beginning of the trip to evaluate everyone’s swimming ability. They took me to the side and said that they remember my “swimming abilities” from the previous years so I could skip it if I wanted to. I said no, I need to get in the water. And I did, and I swam like a fish!
With the saltwater and a wet suit, my new leg muscles were twice as effective as the lap pool. The whole trip I would be first to the whales and the last to return to the boat. I just wanted to swim in one of my favorite places on earth as if I found my home.
2019 was an indescribable experience. The goofy whale sleeping vertically, the curious baby that came right up to the boat, the singer, the breaching adult five feet from the back of the boat, and we were in the water with whales at least 5 times a day.

The second day was when I noticed that my camera housing was leaking, and I didn’t even care. I was finally in the moment and enjoying all of it. The daily swimming had helped tremendously but I think I had also entered a different state of mind. I grabbed the photos I could with the equipment I could afford but the best part of the experience was just being there.





When I got back this time, I couldn’t afford to book another trip right away but I’m hopeful that I can return in 2022.
After this third trip, I tried to share my journey with others. With a lot of experimenting, I decided to print my images on Hahnemühle Photo Glossy. Glossy paper has never been my first choice or even my last choice for printing photographs however I am always learning something new. A print on Hahnemühle Photo Glossy paper beautifully represents the fantasy world of super slick and contrasty computer screens and phones. Hahnemühle Photo Glossy is excellent if you want to proof your images for aluminum printing.
Most people think that my whale images are screen saver shots and the prints just don’t make sense unless they look like a screen. With a glass-like smooth surface, the printed water looks wet, as if you are looking through a window at this incredible world. I think that an underwater image of a humpback Whale is too fantastic to be believable or completely understood.
A female humpback is the size of a school bus and a newborn calf is about the length of a Honda Civic. Photographing whales is like photographing the moon with your longest telephoto and the moon ends up being a small white dot. When I look at my images, they might not be the best whale photographs, but they are my whale photographs and I will cherish them for my lifetime.
It has been an incredible adventure swimming with whales and the stories are much longer than I care to write about. I would rather share my many misadventures on doing something I love along with the successes. Instead of sharing that one good image on Instagram, I hope my stories prove that I can be a little foolish, clumsy, and unsuccessful, and that I’m okay with that. I just keep trying and enjoy every moment of it.
As a photographer, I am grateful for the teachers who lead photography tours and as a photographer, I focus on creating my own vision but also buy other’s work to support their vision. I hear “I’m jealous” or “I wish I could” too often when it comes to photography or adventures. I hear about photographers quitting before they even start because they don’t have the “right” lens or the “right” camera. I also hear “someday” or “maybe when my skills are better.”
The best photographers I know are out there taking photographs with the best equipment they can afford. If it is a phone or the latest full-frame camera, just use it. My thought behind this story is a message to myself as well to others. The light will never wait for you and the moments you miss will be a lost opportunity.
It doesn’t matter how often you fail — just record your own vision and experience and appreciate how wonderful it is.
About the author: John Granata has a long 28 year storied history with photography and currently teaches printing classes at Richard Strongberg’s Chicago Photography Classes in Chicago, Illinois. The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors. He presents a unique argument with an odd mix of technical and emotional reasons why printing is essential to every photographer and has a strong passion to create prints that speak to the viewer. Past projects include photographs taken and processed with that “John” look with several unique alternative printing methods and materials. He has a website that surely needs to be updated and possibly reworked. Currently, he is on hiatus from actively working photographically but is telling stories about past projects in order to rediscover his vision for new ones.
My fascination with documenting the last two remaining northern white rhinos at Ol Pejeta Conservancy in Kenya began in April 2019 as I launched my personal project Kindred Guardians. The project tells the stories of people who have dedicated their lives to helping animals. The caretakers of the rhinos felt like a perfect way to launch the project.
It wasn’t easy to obtain access, as the conservancy is overwhelmed with media requests and there I was without any work in the animal conservation world to show, nothing for the project yet either, and asking for over a week of rare access getting up close and personal with the rhinos and caretakers. I’m not a wildlife photographer, I shoot documentary photography so it’s essential for this project that I can get close to my subjects so I was asking a lot.
It took a lot of back and forth and being persistent, but in the end, it paid off and I booked a flight to Kenya. People have asked me how you get access to something like this and to stories in general. For me, I’m making a career pivot into more personal projects and stories related to people and animals. In the beginning, it was challenging because I had very little work in this field. What I do have is a career shooting for high-profile media clients so I highlight them. However, I never embellish and I never promise or mislead them into thinking the story will run in any of these publications, which is unethical and just plain wrong.
For each chapter of my project, I pitch the stories to media outlets after the fact, not before, and I never make promises I can’t keep. I believe in full transparency about the access I’m looking for and being clear about my process after I’ve finished shooting each story. The disadvantage of doing it this way is obviously that I won’t get my expenses paid for by a publication and it also makes it a lot more challenging to get access as most people and organizations will rightfully wonder what’s in it for them.
The advantage of pitching after the fact and why I take this approach is that I’m photographing this project a very particular way and experimenting with my storytelling style so I don’t want to be beholden to any publication. I realize this isn’t a great financial model but that’s why I do commercial work — to fund projects like this.
A personal project is about experimenting and discovering new things about your craft and when you’re on an assignment you don’t have time to do that. The only promises I make to my subjects is I donate a selection of my images to the person/organization and I do my best to pitch the stories afterward while also promoting on my social media network. I’ve reconfigured my Instagram account to focus primarily on this project and it’s been a rich resource for raising awareness and connecting with people in the wildlife world.

First Visit
I knew right when I arrived in Kenya at Ol Pejeta Conservancy and laid eyes on Fatu and Najin (the last northern white rhinos on the planet) that this story was special and that this wasn’t going to be just a one-time visit.
I’ve covered stories about the illegal rhino trade in Vietnam years ago for TIME magazine and for the UN and it left a mark on me, but this was the first time I’d seen a rhino horn attached to a live rhino and the sadness over the finality of it all felt personal and potent. The whole experience was a whirlwind of emotion; anger and disappointment in humanity and respect and inspiration for the caretakers and rangers.
I spent over a week there documenting the caretakers and rangers and was touched by their dedication and passion for the rhinos. The way my project works is that I typically will only focus on one type of animal and one visit for each chapter but sometimes you must recognize when a bigger story is staring you right in the face, this was one of those times.
Things worked out after that first visit and along with having the first chapter of my long-term project, I got the story published in the Washington Post. They’ve been a great outlet for my project and extremely supportive ever since with several of my other chapters of the project set to be published soon.
I wasn’t the first and only person to cover this story but we got great exposure from my work not just in the Post but I did an exhibition in NYC, a panel talk in NYC on the illegal wildlife trade, and the story also ran in Paris Match and My Modern Met, among others.
Many photographers tend to shy away from doing a story that’s already been done before. It’s something to consider and you never want to repeat or copy other’s work, but stories aren’t owned by any one person. You can always bring a unique angle to a story and do it your way stylistically. That’s the great thing about stories, they can be told so many ways while still be accurate and fair. In addition to that, we live in a new era for self-publishing your work and for reaching people through social media so even if one photographer did the story, you might be able to reach new people and help in your own ways.
I started to build a relationship with Ol Pejeta and we began to collaborate on raising money and awareness about the plight of the rhinos. I stayed in touch with their head of communications Elodie Sampere and she kept me up to date on the latest news about the rhinos.

Second Visit
Months after my first visit I was transiting in Hong Kong and I checked my WhatsApp, Elodie from Ol Pejeta messaged me about a historical procedure they were attempting, a collaborative effort of the BioRescue program, the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW), Avantea, Dvůr Králové Zoo, Ol Pejeta Conservancy, and the Kenya Wildlife Service.

The ovum procedure would involve placing the rhinos under general anesthetic. With an ultrasound to guide them, veterinarians would use a probe to harvest eggs from Najin and Fatu. After the eggs were harvested, they were to be transported to Italy where the embryo would be created. The embryo is stored in liquid nitrogen, the next step would be for the embryos to be transferred to a southern white rhino surrogate mother with hopes for the birth of a northern white rhino calf.

Upon hearing about this Hail Mary attempt, I knew I had to go back to Kenya, but it wasn’t that easy. The decision wasn’t solely up to the conservancy as many organizations and individuals were involved but Elodie fought hard for me to come. For such a procedure like this, it’s extremely stressful for the rhinos and for the veterinarian team so I completely understood their trepidation to have anyone there that wasn’t essential personnel — it’s about trust.
The fate of a species was in their hands and putting such a large animal under anesthesia is always a gigantic risk. One mistake and the population of the species would be down to one, I can’t even imagine that pressure.
Discussions were had and a lot of back and forth and while I missed the first attempt I was granted permission to come for the second attempt along with 2 local photographers and only one other international photographer.
At first, I was conflicted about what kit to bring. For my personal work, I’ve been using a minimalistic set up of a Leica M10D (please let’s not have a Leica debate here in the comments section) coupled with a Leica 35mm, 75mm, and a 135mm. This being an event with other photographers to work around, something I hate doing, I debated taking a more conventional set up of 2 Canons with an army of lenses but I’m moving away from working that way so stayed with my simple set-up. I feel very comfortable with manual focus and with using predominantly a 35mm. I knew the procedure would be covered by 3 other photographers so I could approach it my way with my project in mind but also getting the collaborative team a unique set of images for their press release, something I offered to do.



I spent days leading up to the procedure sharing meals and talking with the procedural team and learning more about their work, incredible, they are the navy seals of veterinarians, scientists, and conservationists traveling the world performing cutting edge procedures to save species from extinction. The procedure was led by Thomas Hildebrandt, Head Department of Reproduction Management at Leibniz-IZW and his team. Hildebrandt also invented the unique system for harvesting the oocytes along with his engineering friends.

I discussed with them about where I could and couldn’t go and they assured me confidently that if I got too close or in the way, they would let me know. Many photographers feel entitled and can be quite aggressive, that isn’t my style nor was this the situation to do that. I respect these guys and was there because they granted me permission and obviously, their work is much more important than mine and the safety of the rhinos is paramount

I was there a few days early to capture some moments between the caretakers and the rhinos before the procedure to help tell the story. Documenting before and after an event was something I learned from my professor at university and it’s always stayed with me. They were tense and obviously worried, the rhinos are like family to these guys as they spend more time with them than with their own families.
The day of the procedure was stressful for everyone, but it went smoothly. They operated on one rhino at a time and each procedure took a few hours to complete. By the second attempt, one of the veterinarians was encouraging and even inviting me to get closer. Being unobtrusive and respectful is the right thing to do and I’ve found it pays off a lot more than being aggressive and entitled.

Just a few hours after the procedure was over I followed the team to the airport where they carried the extracted oocytes to a small plane on their way to Germany through Nairobi and I captured some crucial images to help tell this story.
At the request of the entire collaborative team involved, I waited for them to send out their press release before pitching the story around and sharing any images. After the embargo was listed, the Washington Post ran my images and interviewed me about the procedure. I found my minimalistic kit worked out well for me as it made my move more and think more.

It was an incredible experience to document something so historical and I feel truly honored to be allowed to be there and I never forgot that or took it for granted. They still have a long way to go with this attempt to save the northern white rhino, but I intend to be there every step of the way.
As a documentary photographer, you need to recognize when a story has more to offer and find a way to be there when it does.
About the author: Justin Mott is an award-winning editorial, travel, and commercial photographer and director based in Vietnam for over a decade. The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author. Mott has shot over 100 assignments throughout Vietnam and Southeast Asia for the New York Times covering tragedy, travel, features, business, and historical moments. You can find more of his work on his website, YouTube, Twitter, and Instagram. This article was also published here.
Countless photographs are snapped every day by people looking to preserve their life’s experiences, but is the incessant picture taking actually robbing us of them? Travel photographer and writer Erin Sullivan recently gave this interesting 8-minute TED Talk on the subject.
In growing her popular Instagram account, Sullivan was interested and amused by how many similar photos she found online of the same places she visited and captured.
And after going to famous landmarks and seeing people get out of their cars, snap a photo of the location with their phones, and then get right back into their vehicles, Sullivan began thinking more about this behavior.
Sullivan notes that recent research revealed that photo-taking can increase our enjoyment of experiences. But if a person shoots a photo solely with the intention of sharing it, there isn’t an increase in enjoyment.
“Let me be clear: I am not trying to discourage you from taking photos,” Sullivan says. “Even if thousands of people have been to whatever exact location and taken whatever exact photo, I encourage you to get out and create too. The world needs every voice and perspective, and yours is included.
“But what I’m trying to show you is that the phone or camera doesn’t have to stay out all the time. What I’m trying to encourage you to do is to put it away, just for a moment — a moment for you.
“[…] The next time you [pull out your camera], first stop, pause, take a deep breath, look around. What do you notice? […] Remember that this moment only comes once. Photography can be part of a beautiful experience — just don’t let it be a block between you and reality. Be intentional, and don’t lose a beautiful, irreplaceable memory because you were too focused on getting the shot.”
If you’re getting into astrophotography, the telescope manufacturer Celestron has published a helpful “celestial calendar” to give you a heads up of notable things you’ll see in the night sky through the end of 2020.
The calendar contains events like eclipses, supermoons, and planet oppositions. Each event has a date, description, and information on where on Earth they’ll be visible from.
A detailed calendar and guide can be found on the company’s blog, but there’s also a downloadable compact poster version of the calendar that could look great on your wall.
If you’re looking for info on how to get started in photographing these things, here’s a 15-minute beginner’s guide to astrophotography, here’s a 30-minute guide to buying your first telescope, here’s an article on using a star tracker, and here’s an article on how to photograph night sky objects like Jupiter from your own backyard (for cheap).
Creativity is, in some respects, intangible. It does not have a physical form. It cannot be distilled and sold in bottles. It cannot be summoned at will, and if it does happen to show its face, there is no guarantee that it will stick around.
Creativity is elusive and as such, is one of the pinnacles of photographic achievement.
Many photographers will ask after its whereabouts, and how it might fashion them a personal style, vision, or voice.
“One does not think during creative work, any more than one thinks when driving a car. But one has a background of years – learning, unlearning, success, failure, dreaming, thinking, experience, all this – then the moment of creation, the focusing of all into the moment.” –Edward Weston
Creativity and Fulfillment
Guy Tal once said that the biggest downside to shooting Mesa Arch at sunrise was that you’d end up with a photograph of Mesa Arch at sunrise.
Why? Because the end product is a photograph that has been taken before. A path that has already been walked, sometimes countless times.
Creativity by definition is the process of bringing something into existence that didn’t exist before.
This is easy to do, in theory.
Anyone can go out and take a picture of the clothes on their washing line. Have you created something that didn’t exist before you hung out the washing? Sure did. Creativity? Check.
You’re unlikely, however, to be moved by pictures of your underwear flapping in the breeze. Unless that’s your thing, of course.
Creativity without fulfillment is a waste of time.
Hence, I posit that you need to put yourself in situations that you find fulfilling. Situations where creativity is most likely to come knocking.
How do you do this?
It’s a three-step process, summarised as such:
- Determining your unique attributes.
- Defining your meaningful experiences.
- Refining your creative process.
Determining Your Unique Attributes
The great Ansel Adams was a photographer and environmentalist, as troubled by urban development as he was fascinated by the beauty of the natural world.
What is perhaps less well known about Ansel is that as a child, he was bullied because of learning difficulties and frequently changed schools. He was also thrown from his house during an earthquake aftershock, permanently disfiguring his nose.
While he had professional aspirations to be a pianist, he became interested in the outdoors after he moved to a house with uninterrupted views of the Californian coast.
It was here that his shy, curious nature could flourish.
“(I was) more responsive to wild environments than to urban…the surf and dunes, the storms and fogs of the Golden Gate, the thickets of Lobos Creek and the grim headlands of Land’s End.” –Ansel Adams
Recognizing that Adams gained immense pleasure from more solitary pursuits, his father made the decision to home school him at age 12.
As a result, his father had more of a say in what Ansel would learn. He taught him to live in the vein of Ralph Waldo Emerson – modestly, morally, and guided by social responsibilities to man and nature.
How to discover your unique self.
The first step requires some good old introspection. I’m an introvert, so introspection is like shelling peas.
But for others, it may be less intuitive. Start by looking at what makes you, well, you.
If you like street photography, how did that come about? How has street photography shaped your personality? How has your personality shaped your street photography?
Attributes such as hobbies may be easy to determine.
Other attributes that explain your hobbies might require more insight. These are things such as ideas, values, beliefs, life experiences and even your genetic makeup.
Defining Your Meaningful Experiences
For Ansel Adams, his parent’s decision to buy a house on the Californian coast was a major driver of his love of the natural world.
But this was just the start of his love affair.
At age 14, he took his first trip to Yosemite National Park.
“That first impression of the valley—white water, azaleas, cool fir caverns, tall pines and stolid oaks, cliffs rising to undreamed-of heights, the poignant sounds and smells of the Sierra…was a culmination of experience so intense as to be almost painful. From that day in 1916, my life has been colored and modulated by the great earth gesture of the Sierra.” –Ansel Adams
It doesn’t come much more meaningful than that. The excitement and passion in his words are palpable.
What are your meaningful experiences? Where do you like to be, or what do you like to do often? What activities do these experiences entail?
Note that these can be any activity, not necessarily those where you have a camera in your hand.
Ansel Adams loved nature, but he was focused on becoming a professional pianist for many years before making the switch the photography.
Perhaps your meaningful experience is related to the freedom, isolation, and thrill of flying? Whether that be gliding, sky-diving or hang-gliding – could you incorporate a camera into these pursuits somehow?
Meaningful experiences are those experiences to which, either consciously or subconsciously, you attach emotions to. You feel a certain way just thinking about them.
Refining your creative process
At the introduction to this article, I mentioned that creativity without fulfillment is a waste of time.
I also said that creativity is intangible and almost impossible to summon at will.
Creativity is a bit like the cat in a room full of people who instinctively ignore the cat lovers and showers the non-cattiest person with affection.
Don’t go searching for the affections of creativity. Let them come to you.
Yes, there’s no guarantee that creativity will ever come knocking, no matter how much you try to follow a recipe. But half of the enjoyment of photography is finding out.
Fall in love with the process and you’ll save yourself a lot of pain.
Of one of his most famous works, Moonrise, Hernandez, New Mexico, Adams noted that:
“If I had spent more time in the Chama Valley, I would have missed the entire thing. If I had come home earlier, I would have missed it. So there’s always an element of chance in photography. If you have practiced and practiced, the process is intuitive. You suddenly recognize something, and you react.” –Ansel Adams
Ansel had a familiarity with the landscape, and his equipment, that allowed to him intuitively sense that such a moment was about to occur.
Creativity cannot exist without emotion.
If the sight of your washing on the line does not emotionally move you in some fashion, then you are not going to be unable to translate that emotion into a photograph.
Using a more realistic example, my background is in environmental science. I love plants, animals and hiking in the outdoors.
When I’m hiking, I find myself looking for plants that I can’t identify. Beyond the obvious novelty factor, there’s also a sense of intrigue and curiosity.
I’m also interested in plants that are more familiar to me. I like to ask myself why a particular plant is growing in a certain place, or why it isn’t flowering yet.
My (very simplified) creative process might go something like this:
- My background in environmental science and hiking leads to an interest in plants.
- The interest in plants leads to a curiosity about their ecological function and as a result, their physical form.
- The curiosity in physical form and function builds a picture in my mind about the bush as an ecosystem and the spatial relationships between plants.
- The awareness of spatial relationships leads to the deep, focused observation of the bush. I notice the intricate details of plants. Leaves in various states of decay or the patterns of bark on pine trees. Communities of mosses struggling through the undergrowth.
- The intricate observations of individual plants lead me to start forming narratives in my head. Maybe the mosses are struggling for survival as they huddle together on the forest floor, clinging desperately to the last remnants of winter. Maybe the single green shoot on a tree devastated by fire is a story of hope and renewal.
- Then, photography occurs.
![]()
“The aim of art is to represent not the outward appearance of things, but their inward significance.” –Aristotle
While remarking that I enjoy the Australian bush would certainly be more succinct, it doesn’t explain how it is a meaningful experience for me.
Nor does it separate my meaningful experience from the millions of other people who enjoy the natural world.
Thankfully, this is only one of several meaningful experiences in my life.
My love of storm chasing on lonely desert roads, for example, is derived from many of the same unique attributes that result in my love of the bush.
When you combine subject matter from separate experiences or cross-pollinate them in some other way, the odds of unique, creative photography increase.
In a 1958 documentary, Ansel Adams likened his creative process to music. While he called music the most expressive art form, creative photography would come close if it was practiced for its inherent qualities.
“Well, in music you have this absolutely necessary discipline from the very beginning. And you are constructing various shapes and controlling values. Your notes have to be accurate or else there’s no use playing. There’s no casual approximation.” –Ansel Adams
Indeed, his approach to photography revolved around:
- Previsualisation of an image before it was made.
- Using a handheld meter to estimate exposure and tonal range (the Zone System).
- Meticulous record-keeping of camera settings and zonal range data.
- Meticulous negative quality control – checking for image sharpness and shadow density.
- Maintaining standards comparable to an architect or engineer.
- Many visits to locations to get the right shot in the right conditions.
Ansel had a love for the process – but only in the sense that things should be done properly, or not at all. He believed that there were no half measures in artistic expression.
His meticulous and rigorous attention to detail allowed him to focus on the creative aspects of photography. The stuff that matters.
Case in point — Moonrise, Hernandez, New Mexico. A photographer less familiar with their tools would have squandered the moment. Indeed, the light on the crosses lasted a mere 15 seconds after the exposure was made.
How Else is Creativity Influenced?
Adams was, to some extent, a product of the era in which he was born. A key proponent of his photography involved previsualizing images before he took them. He would then spend hours in the darkroom achieving a realistic interpretation of the images that he saw in his mind’s eye.
Previsualization was particularly useful for Adams because he was devoted to preserving wild areas by communicating their grandeur to others.
Without being crystal clear on how he felt, what he saw, or what he wanted to say, Adams would have failed to inspire many people at all.
If previsualization is one part of the equation, showing up is the other.
No matter how much Adams was excited about the potential of photographing the Sierra Nevada, he still had to physically be there to make the photographs.
Indeed, many of his forays into the mountains were no walks in the park (pun intended). Before he acquired a mule, he carried bulky camera equipment on his back without the assistance of well-formed trails or facilities.
Patience, persistence and hard work were crucial to his success.
![]()
Creativity in the modern age
Have qualities such as patience and persistence fallen by the wayside in modern times?
Is the extent of modern previsualization looking at the same old compositions of the northern lights over the Lofoten Islands?
While Adams was a revolutionary in some aspects, creativity does not require that you reach the same lofty heights.
You just have to use the tools that you’ve been given in life.
Better yet, you have to honor your tools. Give them a chance to shine! What other option is there?
What do you want to say about the world? What do you want to say about yourself?
It might be something that you’re afraid to express. Conversely, something that you can’t express enough.
This may take some time to figure out, but the odds are you have meaningful activities that you haven’t yet associated with photography.
What is it that makes your heart beat rapidly — literally, or metaphorically? Embrace it! There is a good chance it’ll be you.
Conclusion
Creativity is walking your own path, even if, at least initially, you’re pushing through a blackberry thicket.
Creative, meaningful photography ought to be an expression of your uniqueness, rather than a simple reproduction of an aesthetically pleasing scene.
Creativity is a mixture of intuition, instinct, knowledge and meaningful experience. It is not something to be hacked, gamed or bypassed. It requires trust, faith, foresight and a certain tolerance to pain.
Aesthetically pleasing and often classically composed scenes are undoubtedly beautiful, but are they truly an expression of your innermost creativity? Only you can decide.
Don’t rely on external stimuli for your creative angle. Focus on finding your unique attributes and you can unlock the rest of the process from there.
In some respects, Ansel Adams was born to be a photographer. Even though he never made it as a professional pianist, it was his love of piano that instilled in him an understanding of expressive art, devotion to process and a strong work ethic.
These are qualities that are common to many people. But Adams also had environmental values from a young age, and he basically had an out of body experience the first time he saw Yosemite. A camera allowed him to do everything he did with a piano, and more.
About the author: Benjamin Stevens was born and raised in Australia. The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author. Stevens’ college degree says that he is an environmental scientist, but his heart and soul tell that he is a mindfulness photographer and a writer. He mainly photographs nature and landscapes, and you can see more of his work on his website, Instagram, and Facebook. This article was also published here.
Over the last few years, it seems like it’s become really cool to hate Adobe; kind of like how it’s cool to hate Coldplay. Except the main difference is that Coldplay really does suck.
Note: I do not have any kind of relationship with Adobe.
Photoshop Is Still King
Photoshop is probably the most famous editing software in the world. It’s become part of society and has been adopted into our language. Chances are, that it’s more common to say “is that picture Photoshopped” as opposed to asking if it was edited.
If you’re a photographer, then you probably use or have an understanding of how to use Photoshop. It’s pretty much the industry standard now. There aren’t many if any other software’s available which can compete in terms of functionality and features. It’s the most famous photo editor for good reason. Even many of the people who have moved over to Capture One from Lightroom, still use Photoshop; because it’s a difficult piece of software to replace.
At this stage, I doubt I’ll ever change over to any other editing software. This is true even if the alternative is noticeably better. The main reason is that Photoshop is now part of my workflow.
For most people including myself, once you’ve learned one piece of software, it’s extremely unlikely to change over to another. It just isn’t cost-effective to move to another editor because of the time required to make yourself familiar. The learning curve costs time and money. Honestly, Photoshop serves most if not all requirements that photographers tend to have. For that reason, there’s very little need to consider any other option.
Why Lightroom Is Brilliant
My relationship with Lightroom is similar to the one I have with junk food; it’s easy and readily available. I know, that that Capture One is the more professional option and does a better job at developing raw files, but then, I did just eat a whole share bag of crisps.
In all seriousness though, Lightroom is brilliant. It’s still in my view the best software for bulk operations and quick editing. Add the Loupedeck to it and honestly, it’s difficult to compete against when it comes to how easy and straightforward it is to use.
Personally, I’ve spent more time with Capture One, but, even after years of experience with it, I still feel more comfortable with Lightroom. The main reason for this is because Capture One is trying to do a lot more with each update while Lightroom remains exactly what it is. This by no means a point against Capture One, because I prefer it in any logical discussion. What I’m trying to say is that Lightroom does a great job of being easy to edit with.
Being easy to use is an extremely valuable and highly underrated feature.
There are some genuine complaints about Lightroom that need to be addressed by Adobe, but for the most part I still recommend it.
The Best Suite Overall
![]()
The main advantage Adobe has is the fact that it’s a suite. As you grow and develop new skills, you have the tools available to you to continue using Adobe software. For example, I started my career as a photographer and now I also produce video content for my YouTube channel and for many of my clients. Video production is something that generates a great deal of income for me and using Adobe just made the whole process that much easier.
If I need to edit any audio clips, I can quickly take it into Audition and make some meaningful adjustments. I find After Effects to be super useful for timelapses and for making complex adjustments to video clips.
Adobe covers so many requirements for so many creatives that it really is the best suite overall.
The Subscription Model
I don’t understand how any reasonable individual could consider this to be a problem. The subscription model is fantastic. I currently have access to all of Adobe’s software for what is, in my view, an incredibly reasonable price. I mean seriously, what’s the argument against it; you don’t own the software? As customers, we probably don’t own any software we currently use, we merely have a license for it.
The subscription model is a far cheaper option. Previously, you’d have had to buy each individual software at a price that’s more than what the subscription costs over several years. Photoshop alone was priced at around $1,000, which is a lot more than I’d ever want to spend in one go on it.
I understand that some of you may want to argue that, needing to pay regularly, overtime ends up costing more. This isn’t true, at all.
Currently, the photography subscription, which includes Lightroom and Photoshop, costs $9.99 per month. You would need to have the subscription for about 10 years before it ended up costing you more. This also does not include the cost of upgrading to any new versions you may want in those 10 years.
Any argument that is around the price of the subscription model is wholly ridiculous. The subscription has made Adobe software available to far more people than ever before. Students who may have never been able to afford Photoshop now have access to the whole suite. The profits that Adobe is currently generating also prove that this is far more popular than the pricing method they had previously.
This subscription model has also pretty much eradicated the need to pirate the software. The price is so reasonable that people would have stolen the software are willing to pay for it.
Customer Support
![]()
Twice a year, Adobe will do something incredibly stupid and ruin everything. For some reason, this always seems to happen exactly when I’m in the middle of working on a big project. Just when I need everything to run smoothly, Adobe will haphazardly release an “update.”
Personally, I think it’s these incidents that really seem to frustrate many photographers. Adobe seems to think it’s a good idea to change how fundamental features should work.
Seriously, Adobe, get over yourselves and stop tampering with tried and true features. We all hate you for doing it.
Fortunately, the customer support that Adobe offers seems to more than make up for the common blunders inflicted upon its customer base.
I really can’t fault the technical support Adobe offers. They temporarily take control over my computer, fix the fault, and then I carry on. While I’m making a cup of coffee, the support team sorts out any problems — I really can’t complain about that.
There isn’t a company on the market that hasn’t had technical issues with the service they offer. There are, however, many companies that offer worse customer support than Adobe by a significant margin.
Final Thoughts
Adobe now has the largest customer base. More people use Photoshop and Lightroom than any other photo editor on the market. When you have a huge customer base, a small percentage equates to a significant number of individuals. My guess is that most people are happy using the software and it’s simply a vocal minority that dislikes or hates Adobe.
I appreciate that there are lots of things that Adobe still needs to improve, but I’m optimistic about it. There’s more competition in the market now than ever before and if Adobe doesn’t keep up the pace, then customers can simply move. We’ve already seen plenty of people moving away from using Lightroom.
I’m certain that some of you will claim this is a sponsored or affiliated post, but it’s not. I’m just baffled whenever I see people being so aggressively against Adobe for such minor issues.
Ultimately, Adobe offers some of the best software on the market and the new subscription model is simply wonderful.
The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author.
About the author: Usman Dawood is the lead photographer of Sonder Creative, an architectural and interior photography company. You can find more of his work on his website, Instagram, and YouTube.
Astrophotographer Ian Norman of Lonely Speck recently got his hands on a Google Pixel 4 XL for testing, so he took it out to Joshua Tree National Park to see how well the “Astrophotography Mode” on this smartphone compares to shooting with a “real” camera.
Right off the bat, it’s important to note that Ian successfully shot some impressive smartphone astrophotography long before Google baked this feature into a flagship phone. Still, the improvements that Google has made in this area are significant, and at first glance, the resulting images are staggeringly clear.
Upon closer inspection, Ian did find that the images are definitely not as sharp as what he was capturing with his 12MP Sony a7S—perhaps due to missed focus, perhaps due to the optics in the phone—but when you down-res for Web comparison the results Ian shares in the video are still strikingly similar:
![]()
Ultimately, while the lack of creative control in Astro mode can be a bother—no control over things like white balance or shutter time, and limited control of focus—the Pixel 4’s fully-automatic Astro mode achieves something really cool: it makes astrophotography significantly more accessible. A “gateway drug” most astrophotographers can probably get behind.
Check out the full video up top for a full evaluation of the Google Pixel 4’s Astrophotography mode, complete with multiple sample images, workflow footage, and lots of 100% crops so you can see where the smartphone camera fails to keep up with its full-sized rivals.
And if you’re an astrophotography buff, definitely check out Lonely Speck. Ian’s educational content is second to none in that space.
(via Fstoppers)
In my early years of photography, I was very concerned with making “ART.” Each time I would pick up a camera I would be filled with anxiety, thinking that I need to bring home that “picture of the century.” I have to tell you, I seldom did.
One of the most important lessons I’ve learned over the years is not to worry too much about the end result—instead, I’ve learned to trust the process.
![]()
My Process
For me, the process often starts with either an idea or (more often) a vision. I have a flash of a visual sensation or an actual picture in my head that I want to create. I then ask, what do I need in order to create that image.
The first questions are: do I need subjects, a certain location, certain objects, a particular color scheme or type of light? And, if my idea is more editorial (i.e. “people who surf while standing on their heads”): will this require me to recruit or discover certain types of people?
The next list of questions are more logistical: what type of equipment will I need? Will this image require an unusual camera, grip and lighting gear? Will I need a crew or will my “one-man-band” be all that is needed?
Next, I envision and think about the final image and ask: will this picture I am trying to create require a different approach to the post-processing work? Often this question does not get asked until after the actual shoot.
At this point, the questions become more personal. Is the image I want to create an endpoint or the start of a visual exploration? These two different goals require different mindsets. If I am after a very specific image, the process becomes getting stuff out of the way. If I’m exploring, then I need to keep my eyes and my heart open to all possibilities.
![]()
“Do the Work”
In Julia Cameron’s book The Artist Way, she talks about how the job of the artist is not to critique their own work but to simply “do the work.” There are many, many souls who will offer their two cents and will be more than happy to build roadblocks for you. The photographer’s job, any creative person’s job, is to ignore these well-intentioned friends and pursue the vision.
I have found that if I follow my creative process then I need not worry about these often self-imposed barriers. In the end, I believe it is the artist job just to pick up that pen, paintbrush or camera and go do the work.
Living is learning how to be comfortable in one’s own skin. Living is learning when to trust and when to be wary.
I no longer get up in the morning and think, “I need to make great art today!!” Instead, I’ve learned to trust and follow my creative process. I’ve learned not only to focus on the outcome, but to also enjoy looking out the window during the journey and to trust that if I follow the process, I will often create something worthwhile.
About the author: Zave Smith is a passionate photographer who was raised and trained in the Midwest, and is now based out of Philadelphia and New York. You can find more of his work on his website, Instagram, and Facebook.
YouTuber Tyler Stalman recently got his hands on a review unit of both the Mac Pro and the Pro Display XDR, and while many tech YouTubers have reviewed these extreme (and extremely expensive) Apple products, he’s the first we’ve seen who’s evaluated them from the perspective of a professional photographer.
The full video speaks to all “professional creatives,” including video shooters, so it’s all there if you want. But Stalman starts off right away by reviewing the Mac Pro (with a nod to the Pro Display XDR) for studio photography.
![]()
Stalman explains that the review unit he has is “overspecced” for photography—with its 16-core 3.2GHz Intel Xeon processor, 192GB of RAM, Afterburner Card, and not one but two Radeon Pro Vega II graphics cards with 32 total gigabytes of VRAM—but he still enjoyed the ridiculous headroom this offered.
Despite processing 16-bit TIFFs in CaptureOne and Lightroom on one screen, messing with a 100MP photo in Photoshop on another, rendering a video out in Resolve, and playing back footage in Final Cut all at the same time, the computer never had to use more than 70GB of its RAM. Even when all of the CPU cores were at full load.
Lightroom Classic (surprise, surprise) did start getting a little jittery at one point, but that’s because it’s simply not well optimized. The computer’s hardware simply wasn’t ever fully taxed by the kind of work a professional photographer—almost any professional photographer—would do.
![]()
For photographers, the conclusion is pretty clear:
“There are very few photographers out there who can really tap into the potential of what this can do maxed out. The ultimate power in here is really for 3D or Video,” explains Stalman. “Even if you’re shooting on a Hasselblad or a PhaseOne and you’ve got 100MP+, it seems to handle it perfectly.”
Check out the video up top to see all of these tests in action and watch Stalman build his “ideal” Mac Pro for a budget conscious professional photographer. Of course, “budget conscious” is a relative term here (calm down PC enthusiasts), but it’s clear you don’t have to (and shouldn’t) get anywhere near the max price of $52,000 if you want a Mac Pro for studio work and photo editing.
(via ISO 1200)
Profoto has finally announced Android support for the battery-powered B10 and B10 Plus monolights, giving Android users control over almost all of their flash settings via the free Profoto Control app.
This feature, which has been available for iPhone users since the launch of the B10 (and later, the beefier B10 Plus), allows you to “easily view and control all B10 and B10 Plus settings from the palm of your hand,” as well as install new firmware updates instead of going through a huge cumbersome process.
Here’s a look at the app in action, so you can get a sense of what all is available:
It’s not a huge update, but it’s a welcome workflow perk for photographers who use Profoto and own an Android phone. To try it out for yourself, download the latest version of Profoto Control over on the Google Play store.
Portrait photographer Miguel Quiles recently released a two-part series on “portrait hacks” that might be his most popular series of tips ever. In the videos, he covers 10 tips from his years of experience shooting and teaching workshops—tips that he says “everyone wishes they knew sooner.”
Part 1 was released back in March of 2019 and became one of Quiles’ most watched videos; it covers the most basic tips that will help total beginners understand what they should focus on when shooting a portrait. Part 2 was released this morning, and it gets a little more advanced, covering hacks that fall into the “oh, I never thought of that” category.
You can watch Part 1 up top, and Part 2 below:
For those people who prefer reading to watching, the 10 tips/hacks are as follows:
Part 1
- Fill the frame – Beginners tend to leave a ton of headroom above their subject, this isn’t necessary.
- Pay Attention to Catchlights – There’s no better way to “hook your viewer” and “hold their attention” than great catchlights.
- Eye Placement – Pay close attention to where your subject is looking. They don’t have to look at the camera, but the Iris of the eye should be more prominent than the white Sclera.
- Focus on Lighting – Simple, but it has to be said. A great portrait is all about great lighting.
- Draw Out a Great Expression – Don’t get so caught up in your location or the lighting or your settings that you forget to help your subject relax and get into the shoot.
![]()
Part 2
- Use Continuous Drive Mode – Don’t limit yourself to single shot. Light permitting, shooting in Continuous mode can help you capture expressions that you might otherwise miss.
- Develop Your Poker Face – Portrait shoots are stressful, but don’t let it show on your face! If you look stressed while you’re shooting or reviewing images, your subject will tense up.
- Use the ‘Eye Chart’ Technique – Tell your subject to pretend like they’re looking at an ‘eye chart’ at an eye exam. This is a brilliant way to prevent that wide-eyed Deer in the Headlights look.
- Tether Whenever Possible – Having a big screen to review your images gives you extremely valuable insights into how the shoot is going and how your images are turning out.
- Role Play – Have your subject play a character. It’s one of the easiest ways to help someone get out of their own head and look much more relaxed and natural on-camera.
![]()
If you have the time, you’ll definitely want to watch the videos. Quiles dives into each of these tips, sharing sample photos, behind the scenes video, and stories from his professional work that explain why and how you should follow each piece of advice.
And if you like Quiles style, you can find more of his work on his Instagram, and many more tutorials over on his YouTube channel.
Image credits: Photos by Miguel Quiles and used with permission.
Nikon Japan has published a notice indicating that the long-awaited NIKKOR Z 70-200mm f/2.8 VR S lens will have to be awaited a tiny bit longer. The lens, along with its three main accessories, have been delayed and will not be shipping on February 14th as previously announced.
The $2,600 70-200 lens for Nikon Z-Mount cameras was announced on January 6th with an expected ship date of “February.” However, it seems the lens’ production in Japan either can’t keep up with demand or has hit an unexpected roadblock.
“The release date of the NIKKOR Z 70-200mm f/2.8 VR S lens, which was announced to be released on February 14, 2020, has been postponed due to production reasons,” reads the Google translation of the notice posted by Nikon Japan. “We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause to customers waiting for this product.”
In addition to the lens, its lens hood, lens cap, and lens case are also delayed, which is unsurprising.
Unfortunately, Nikon has not established a new ship date for the lens and associated products, saying only that, “the release date will be announced once it is confirmed.” We’ve reached out to Nikon Inc. to confirm that this delay will affect shipments world-side, as well as how long the delay might last, and will update this post when we hear back.
UPDATE: Nikon Inc. has responded to our request for comment and provided the following statement:
We apologize for the delay of the NIKKOR Z 70-200mm f/2.8 VR S lens. We are currently making final adjustments as part of our production process in order to ensure the highest quality product. We will provide availability as soon as possible.
(via Nikon Rumors)
As a landscape photographer I’m a big fan of grand vistas and photographing with wide angle lenses. But sometimes the smaller things can be just as impressive. In this little article I’ll be sharing some tips that will hopefully give you some inspiration when photographing abstracts. And when you start to see them, you can’t stop photographing them. It’s very addicting!
1. Look down
We tend to look forward and see the bigger picture, but beauty is often just at our feet. Go low to the ground and look down occasionally. You’ll find all kinds of interesting things. Think of textures on stones, lines little plants, patterns, contrast. Lots of interesting abstract shapes can be found on the ground.


2. You don’t need a macro lens
Abstract landscapes can be shot with any kind of lens. I usually shoot them with a 24-70 (close focus is a pre-requisite) or sometimes a longer lens to capture patterns in the distance.

3. Look at lines
When looking at subjects, find lines and try to balance them in your frame. Lines going from a corner into the frame often work well. Flowing lines also give a nice feel to an image.



4. Look at color and contrast
A combination of two distinct colors or dark and bright tones often work well in abstracts.


5. Lose perspective and scale
This has to do with looking at the smaller things in the “bigger” picture again. When photographing abstracts, it’s important to not show the surroundings. This way the viewer has no idea about the scale and perspective.
When you photograph a sand texture the right way, for example, it can look like a desert from above. It’s fun to trick the viewer and let them think about your photo.

6. Find single objects in negative space
Showing a lot of emptiness in the frame with a small subject makes for a nice abstract look.
![]()
![]()
7. Go to the beach!
The beach often has lots of sand textures. Especially when the tide is low, you can find patterns in the sand everywhere. They sometimes look like aerials, allowing the viewer to completely lose perspective.

8. Water.
Water by itself is just incredible. Think of falling water from a waterfall or just the tap at home! Falling water in different strengths creates beautiful patterns. When photograph falling water, use an extremely fast shutter speed (1/1000 or faster) and just shoot away. You’ll see you come up with lots of interesting shots!
But not only falling water. Ripples in the sea can create interesting photos depending on how the waves are behaving and how the light hits. And then there is frozen water—frozen water creates cracks and interesting ice textures.



9. Harsh light and shadows.
Harsh light during the day is often not great for landscape photography, but it can be great for abstracts. By playing with shapes and lines in harsh shadows you can sometimes create interesting abstract looks.

10. Look up close.
Abstract landscapes are everywhere, you just have to learn to see them: textures in stones, lines in plants, clouds. The trick is to look closely. Look closer at everything you see in daily life and you’ll be surprised how many interesting things you see.
But be careful, it’s very addicting! :)
About the author: Albert Dros is an award-winning Dutch photographer. The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author. His work has been published by some of the world’s biggest media channels, including TIME, The Huffington Post, The Daily Mail, and National Geographic. You can find more of his work on his website, or by following him on Facebook and Instagram. This post was also published here.
The crash that killed Kobe Bryant, his 13-year old daughter Gianna, and seven others aboard a helicopter shocked millions around the world. Near the Staples Center in California where Bryant played for 20 years as a member of the Los Angeles Lakers, make-shift memorials appeared. And online, fans posted messages of grief and condolences on social media.
Unsurprisingly, images of Bryant were widely shared as if a way to collectively remember him through the most accessible and visceral medium available to us – photography. And photographers who had the opportunity to shoot Bryant during their careers expressed a connection for having done so. Even in the most public of settings, there is something intimate about taking someone’s photo.
Before delving into the topic more deeply, I want to acknowledge that Bryant was an imperfect man with a troubling incident in his past. In 2003, Bryant was credibly accused of sexually assaulting a 19-year old hotel employee, who subsequently dropped the charges despite a mound of physical evidence. Washington Post columnist Barry Svrluga articulated the confounding complexity of Kobe’s legacy:
“In any remembrance of Kobe Bryant, there is the obligation to mention his five NBA titles, his 18 all-star selections, his Academy Award, the sexual assault allegation against him, his MVP award, his four daughters, his second act as a Hollywood mover and shaker, when basketball became secondary. Add all those things up, and out comes the totality of a life — a life with layers, a life with chapters.
…To say that last point makes him “complicated” is a convenient way of minimizing the incident in a Colorado hotel room in the summer of 2003, when Bryant had sex with a 19-year-old woman…Fit that encounter and that admission into the totality of Bryant’s life however you want. In the scope of 41 years — of a basketball career and fatherhood, of a creative and competitive creature — maybe it shouldn’t be solely defining. But maybe, too, it shouldn’t be completely drowned out by the torrent of accomplishments and adulation.”
Barry Svrluga, The Washington Post
Why does a blog dedicated to photography need to cover this? Because photography and culture are inexorably intertwined. A “hero image” that lionizes Bryant can be used to put him on a pedestal, inspire millions, or sell shoes. A photo of him and his daughter can serve as both a memorial and as a shield against past transgressions. And when it comes to a public figure, we have to critically consider our reactions to portrayals of them.
It’s difficult to understate Bryant’s global reach. In China, his jersey outsold those of Yao Ming, and his popularity paradoxically rose in retirement. He was arguably the first global superstar in the age of social media, and if you’re not a basketball fan, it might be hard to understand why Bryant’s death has been so significant to many, and one of the few events to displace political coverage in the news cycle.
Bryant had an extremely long career with a single team (a true rarity in today’s pro sports world), which gave photographers ample opportunity to photography him throughout the years. It was a real treat to see how friends on social media dug up images from the archives to remember Bryant. The practice of posting photos (particularly selfies) upon someone’s passing has become social currency and social proof of both connection and personal relevance. The act might be construed as partially egotistical, but I think it’s mostly a human desire to feel connection to others.
Here are a few of my favorites:
- In 1995, Al Tielmans received an assignment to photograph a high school kid who was entering the NBA a draft – a rarity then and now. His portrait of Kobe dunking is sublime.
- Robert Beck is no stranger to California sports, and he covered both game action and portraits for Sports Illustrated.
- The Los Angeles Times’ Jay L. Clendenin posted a haunting polaroid of a flag draped Kobe.
- Michael Mueller’s photo of Kobe taking a bow earned him the cover of TIME.
- If they visited the White House, Pete Souza has the goods. Most depictions of Kobe are in and around the basketball court, so it’s so great to see this image of him and President Obama.
- Maryanne Golon, Assistant Managing Editor and Director of Photography for the Washington Post, posted this selfie from a newsroom visit. While imperfect from a technical perspective, the inclusion of her in an unplanned photo makes it all the more meaningful.
- DOP/Director Vincent Laforet worked with Kobe for a Nike commercial, and recounted how they worked around Bryant’s broken knee for the shoot.
- Andrew D. Bernstein serves as team photographer for the Lakers, Clippers, Kings and Sparks, and posted this portrait “when our journey started together.”
- Back when Paul Morse worked at the LA Times, he caught Kobe looking out a window. A masterful candid.
- Los Angeles Times staffer Wally Skalij shared some of his favorites from over the years.
- Sports photography was and continues to be largely the realm of male photographers. Elsa Garrison is one of the exceptions, and an exceptional photographer. Her image of Kobe and Gianna is both beautiful and heartbreaking.
RIP Kobe.
About the author: Allen Murabayashi is the Chairman and co-founder of PhotoShelter, which regularly publishes resources for photographers. The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author. Allen is a graduate of Yale University, and flosses daily. This article was also published here.
Image credits: Cover image of the 2002 NBA Finals by Allen Murabayashi.
Kodak has inked a new deal with five of the six major movie studios, re-upping an initial agreement made in 2015 and ensuring that we won’t see celluloid completely replaced by digital in Hollywood any time soon.
The Hollywood Reporter broke the news yesterday ahead of the expected announcement at the Fourth Annual Kodak Film Awards last night. Details are slim, but we know that five major studios — Disney, NBCUniversal, Paramount, Sony, and Warner Bros.—have all committed to buying “undisclosed amounts” of motion picture film from Kodak moving forward.
How long this particular deal is set to last, or what kind of impact this will have on Kodak’s bottom line are unknown. But Kodak says that it “has seen a substantial increase in film sales each year for five consecutive years,” and these new agreements will ensure that this trend continues upwards.
Stills photographers with no attachment to motion picture film might be tempted to ask “so what?” at this point. But as our friends at EMULSIVE point out, a victory for motion picture film is a victory for all film: stills included.
Increased demand for film of all kinds helps keep the medium alive, whether that demand is coming from a younger generation of fresh film lovers, or Hollywood titans like Quentin Tarantino.
(via EMULSIVE)
Image credits: Photo courtesy of Kodak.
If you’re new to digital photo editing you’ve probably had this experience: you export a perfectly edited photo, but the JPEG looks all “wrong”—the colors are totally different! Actually, they not. As Unmesh Dinda from PiXimperfect explains, you just haven’t sorted out your color space properly.
Seasoned photographers and Photoshop users are well-aware of color space, but almost all of us made this mistake as a beginner. The issue, as Dinda explains in the video above, is that you probably exported your photo without first converting it to the most common and widely-supported color space: sRGB.
The three main color spaces used by photographers—sRGB, Adobe RGB and ProPhoto RGB—can each display a different range of colors. sRGB is the most limited, but it’s also the most widely supported; Adobe RGB is next; and ProPhoto RGB is so massive it actually covers colors that aren’t even visible to the naked eye.
![]()
Issues arise when you edit a photo in ProPhoto RGB or Adobe RGB, export the photo as is, and then try to post it online. Not all browsers, apps, or social media platforms will be able to display the wider color space, and will instead display the image as sRGB, leading to a dull or flat looking photo.
You can save yourself the trouble by converting to sRGB at export and ensuring the widest possible compatibility. In some cases, just embedding the ICC profile is enough, but for most web-based photo sharing, you’ll want to convert to sRGB at export unless you want a large percentage of people to see it all “wrong.”
To dive a bit deeper into this subject and learn how to make sure all of your exports look “right” no matter what app or browser or social platform your audience is using, check out the full video up top.
(via Fstoppers)
A Chicago couple is being flamed online after their email to a wedding photographer went viral on Reddit. The email asks the photographer to shoot a 10-hour wedding in exchange for promotion to “300 total wedding guests,” 117 of whom are unmarried and between the ages of 24 and 35.
Wedding photographers being asked for freebies in exchange for exposure is absolutely nothing new, but this request is unusual in its level of sheer demographic detail and how little value is even being offered. Even the wording sounds more like a PR pitch than a typical request.
“We are asking your help to sponsor 10 hours of continuous photography coverage,” reads the email, which has received over 900 upvotes on the r/ChoosingBeggars subreddit. “In exchange, we will be showcasing your company to: 3,000+ combined FB followers, 300 total wedding guests […] 117 unmarried guests between the ages of 24 to 35 years old, [and] 73 parents with unmarried children between the ages of 24 and 35 years old.”
![]()
Additionally, the couple promises to include the photographer’s logo and details in their “wedding brochure,” which will be “distributed to all 300 wedding guests.”
As you might imagine, the response on Reddit has been anything but kind. Several commenters pointed out that other guests would no doubt also ask for a freebie, while others balked at the idea of trading 10 hours of work—plus hours of post-processing—in exchange for “exposure” a social media audience of just 3,000… which probably includes everyone who was invited to the wedding.
You can read the full email for yourself here, and while we can’t be certain, it’s probably safe to assume this photographer decided not to take the couple up on their offer. Fingers crossed nobody else did either.
Yesterday, the U.S. Secretary of the Interior officially signed an order temporarily grounding all Chinese-made drones in the government’s fleet, solidifying a ‘pause’ that was first announced in October and drawing a heated response from market leader DJI.
The official order (embedded below) calls for the “temporary cessation of non-emergency unmanned aircraft systems fleet operations” in order to ensure that “cybersecurity, technology and domestic production concerns are adequately addressed.”
“In certain circumstances, information collected during UAS missions has the potential to be valuable to foreign entities, organizations, and governments,” reads the order. “Pending further guidance based on completion of an ongoing review, the fleet is grounded with the exception of emergency operations described in guidance to be issued by the Assistant Secretary – Policy, Management and Budget (AS – PMB).”
In a press statement posted to the DOI website, spokesperson Carol Danko clarified that this order only applies to “non-emergency operations,” so government drones used for fighting wildfires, search & rescue, and helping with natural disasters “that may threaten life or property,” will remain operational during this investigation period.
DJI has been opposed to these rules from the beginning, and this latest update is no exception. The company quickly issued a statement yesterday saying that it was “extremely disappointed” by the order because it “inappropriately treats a technology’s country of origin as a litmus test for its performance, security and reliability.”
“The security of our products designed specifically for the DOI and other U.S. government agencies have been independently tested and validated by U.S. cybersecurity consultants, U.S. federal agencies including the Department of Interior and the Department of Homeland Security,” reads the statement, “which proves today’s decision has nothing to do with security.”
Instead, DJI is accusing the US of using cybersecurity as an excuse to stifle competition and give US-based drone makers a chance to catch up to the Chinese company’s market dominance.
“We are opposed to the politically-motivated country of origin restrictions masquerading as cybersecurity concerns,” concludes DJI, “and call for policymakers and industry stakeholders to create clear standards that will give commercial and government drone operators the assurance they need to confidently evaluate drone technology on the merits of performance, security and reliability, no matter where it is made.”
There is no official word on how long this “temporary” ban is set to remain in effect, but it will take a new order from the Secretary of the Interior to overturn it, so for now the answer is “indefinitely.”
Image credits: Header photo by Karl Greif, CC0
Indian wedding photographer Ankita Asthana recently traveled to Rome for a shoot and brought along the $8,000 Nikon NIKKOR Z 58mm f/0.95 S Noct lens to test out. She shares her thoughts and a behind-the-scenes look at the shoot in this 7-minute video.

“My first impression is that I am truly impressed by this lens,” Asthana tells PetaPixel. “Impressed by its optical image quality.
“The thing that makes this lens stand out is that it gives no chromatic aberration, no fringing that I could observe. Another thing is that it is almost absolutely distortion-free. You can capture really clean straight lines.”
![]()
![]()
“This lens also has a very close focusing distance,” Asthana says. “That helps in going close and capturing just the eye! At f/0.95, it gives a gorgeous bokeh and, if you nail the focus, a beautiful image.”
![]()
![]()
“It is completely manual focus, but I like that because it gives me a challenge when I shoot, and by not relying on autofocus, you can choose exactly where you want the focus to be,” Asthana continues. “They have given a digital display to help with the focusing, and you can set the focus at a distance that you want.
“It gives sharp edge-to-edge details, even around the corners of the image. The razor-thin depth of field is to die for!”
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
“I photographed a lot of my subjects at night after the sun went down and was surprised at what I could achieve with this lens in low ambient light,” the photographer says. “It is really true to its name — Noct, Nocturnal!”
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
“The downside is the weight of the lens, which is a lot, and it is not made for long hours of shooting handheld,” Asthana says. “If you use it right for a few specialty shots, though, it is quite manageable.
“The result more than makes up for its weight. After I shot for a few days on this lens, I almost didn’t feel like picking up any other!”
![]()
![]()
![]()
“Possible uses in weddings are in low light conditions and tight spaces,” Asthana concludes. “Also for engagement sessions and couple shoots.
“I can’t wait to try it at real weddings. I love the magnification of 58mm — not too tight, not too wide, it is the perfect lens for portraiture. It could also be put to good use while capturing nightscapes and astrophotography as well.”
You can find more of Asthana’s work on her website, wedding Instagram, and personal Instagram. If you’re interested in dropping 8 grand on this lens yourself, you can do so here.
The National Solar Observatory has just released the highest resolution images and video ever taken of the sun’s surface. The images, captured with the National Science Foundation’s Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope, capture the sun in unprecedented detail, revealing features as small as 18 miles (30km) in size for the first time ever.
The 4-meter Inouye Solar Telescope sits near the summit of Haleakala, Maui, in Hawai‘i, and these incredible images of our sun are its grand debut to the world.
“Since NSF began work on this ground-based telescope, we have eagerly awaited the first images,” said NSF director France Córdova in a press release. “We can now share these images and videos, which are the most detailed of our Sun to date. […] This telescope will improve our understanding of what drives space weather and ultimately help forecasters better predict solar storms.”
“It’s all about the magnetic field,” explains Thomas Rimmele, director of the Inouye Solar Telescope. “To unravel the Sun’s biggest mysteries, we have to not only be able to clearly see these tiny structures from 93 million miles away but very precisely measure their magnetic field strength and direction near the surface and trace the field as it extends out into the million-degree corona, the outer atmosphere of the Sun.”
You can see the two images in full resolution below (click to enlarge):
And here is a graphic that puts the images into proper context. The telescope is able to image a piece of the sun that’s just 36,500km wide. “These images show large cell-like structures hundreds of kilometers across,” explains the NSF, “and, for the first time, the smallest features ever seen on the solar surface, some as small as 30km.”
Finally, the group has also released multiple videos. The close up below was taken at a wavelength of 705nm over a period of 10 minutes, and shows “features as small as 30km (18 miles) in size for the first time ever.”
“The movie shows the turbulent, ‘boiling’ gas that covers the entire sun. The cell-like structures – each about the size of Texas – are the signature of violent motions that transport heat from the inside of the sun to its surface,” reads the caption. “Hot solar material (plasma) rises in the bright centers of ‘cells,’ cools off and then sinks below the surface in dark lanes in a process known as convection.”
It’s difficult to understate how important this telescope is for solar astronomy.
“These first images are just the beginning,” said David Boboltz, program director in NSF’s division of astronomical sciences. “The Inouye Solar Telescope will collect more information about our Sun during the first 5 years of its lifetime than all the solar data gathered since Galileo first pointed a telescope at the Sun in 1612.”
For most of us, the Inouye Solar Telescope just means some really cool imagery. But for the astronomical community, it promises to usher in “a new era of solar science and a leap forward in understanding the Sun and its impacts on our planet.”
Image credits: Photos and video by NSO/AURA/NSF, CC BY 4.0.






























 Already reeling from the coronavirus pandemic, schools in rural areas like Bonny Doon must now contend with wildfires and related problems like blackouts, poor air quality and damaged internet infrastructure. ]]>
Already reeling from the coronavirus pandemic, schools in rural areas like Bonny Doon must now contend with wildfires and related problems like blackouts, poor air quality and damaged internet infrastructure. ]]>


 After a spring of crisis education, teachers’ unions hope to parlay many successful reopening battles into bigger electoral victories. But they're also bracing for layoffs of up to 60,000 educators, and some teachers are still scrambling for bare-minimum supplies.]]>
After a spring of crisis education, teachers’ unions hope to parlay many successful reopening battles into bigger electoral victories. But they're also bracing for layoffs of up to 60,000 educators, and some teachers are still scrambling for bare-minimum supplies.]]>

 Fixing poor ventilation in classrooms may slow the spread of COVID-19 when children and teachers return, and create new job opportunities.]]>
Fixing poor ventilation in classrooms may slow the spread of COVID-19 when children and teachers return, and create new job opportunities.]]>

 A fee added to utility bills — less than $1 per month — would be extended until 2045 if the legislation is adopted by two-thirds of both chambers.]]>
A fee added to utility bills — less than $1 per month — would be extended until 2045 if the legislation is adopted by two-thirds of both chambers.]]> ]]>
]]> ]]>
]]>






 It’s critical that we encourage the early adoption of any successfully developed COVID-19 vaccine and promote the widespread use of the flu vaccine.]]>
It’s critical that we encourage the early adoption of any successfully developed COVID-19 vaccine and promote the widespread use of the flu vaccine.]]>

 Health care workers make up nearly 40 percent of those seeking wage and medical benefits from the program.]]>
Health care workers make up nearly 40 percent of those seeking wage and medical benefits from the program.]]> There’s no doubt we need to address the rise in youth vaping, but ban on flavored tobacco will impact small businesses.]]>
There’s no doubt we need to address the rise in youth vaping, but ban on flavored tobacco will impact small businesses.]]>
 If there is an American Indian Studies department at UC Long Beach, it could utilize this land for classes, writing and cultural inclusiveness.]]>
If there is an American Indian Studies department at UC Long Beach, it could utilize this land for classes, writing and cultural inclusiveness.]]>

 ]]>
]]>

















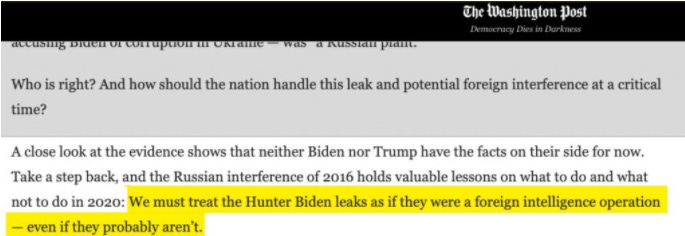



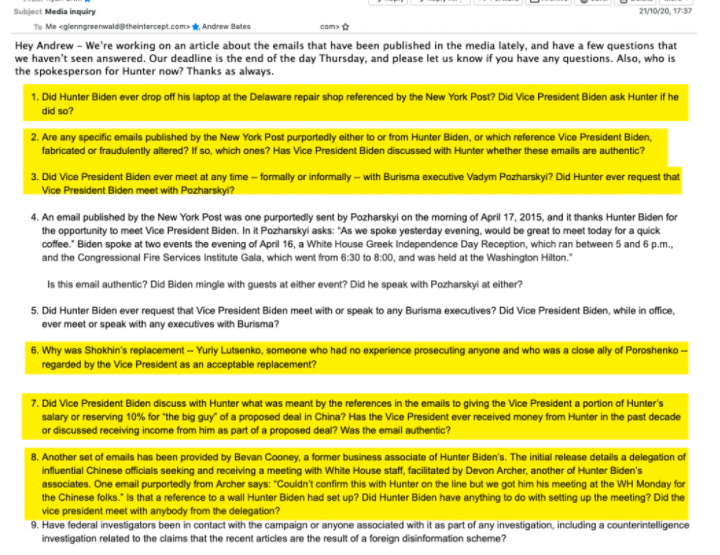
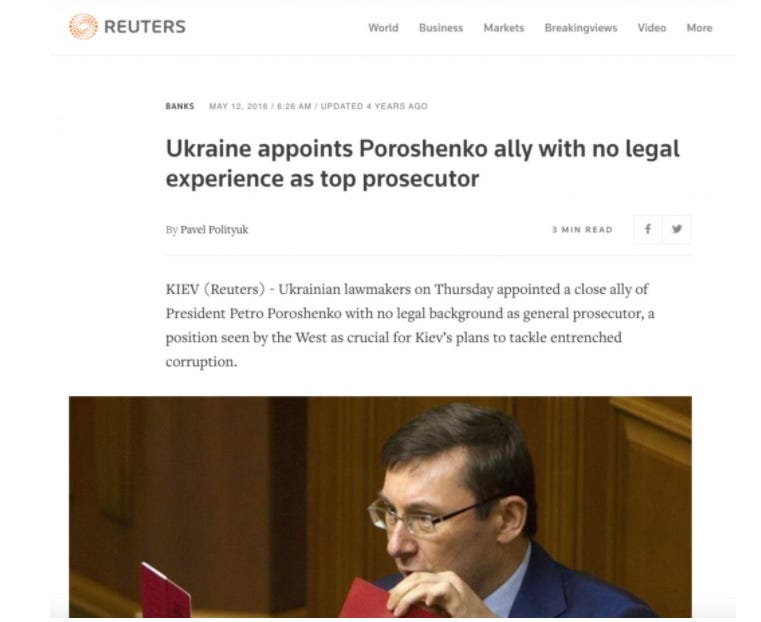


















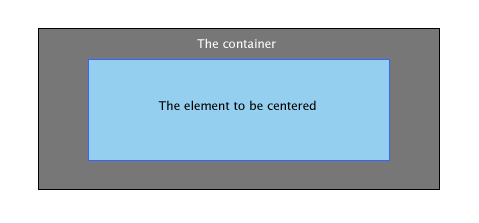


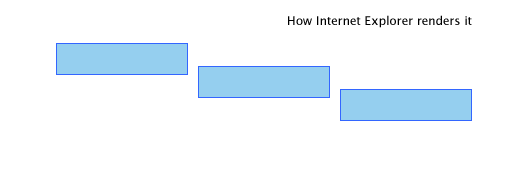






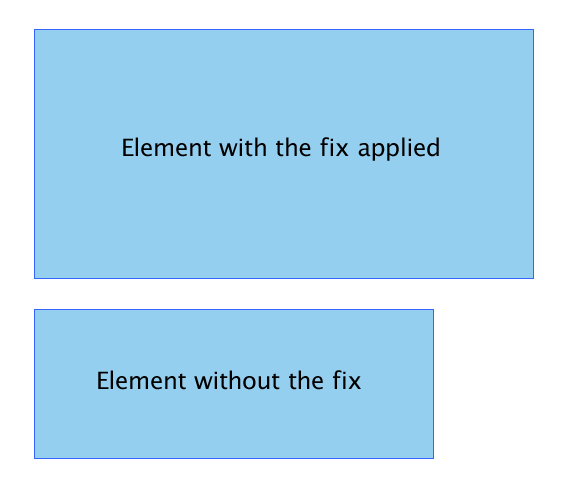
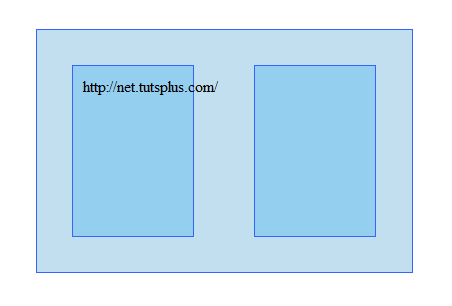














































![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/blog/media/twittergraph.png)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/blog/media/ipad.png)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/blog/media/crunchpad.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/blog/media/feedburner-twitter.png)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/blog/media/aolbluemonster.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/images/altair/page33_thumb.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/images/altair/page34_thumb.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/images/altair/page35_thumb.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/images/altair/page36_thumb.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/images/altair/page37_thumb.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/images/altair/page38_thumb.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/images/altair/page39_thumb.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/images/altair/page40_thumb.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/blog/media/android_big.jpg)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/blog/media/twitter.png)
![[image]](http://www.russellbeattie.com/blog/media/qlauncher3.jpg)
 In his carefree, gung-ho way, JLT liberally bestowed author accounts on those he respected in the realm of typography and encouraged them to post whatever they wanted on the site. News and discussion sparked quickly. Smart, opinionated folks from all corners of the type world contributed to what became an bustling throng of obsessive voices.
In his carefree, gung-ho way, JLT liberally bestowed author accounts on those he respected in the realm of typography and encouraged them to post whatever they wanted on the site. News and discussion sparked quickly. Smart, opinionated folks from all corners of the type world contributed to what became an bustling throng of obsessive voices. 